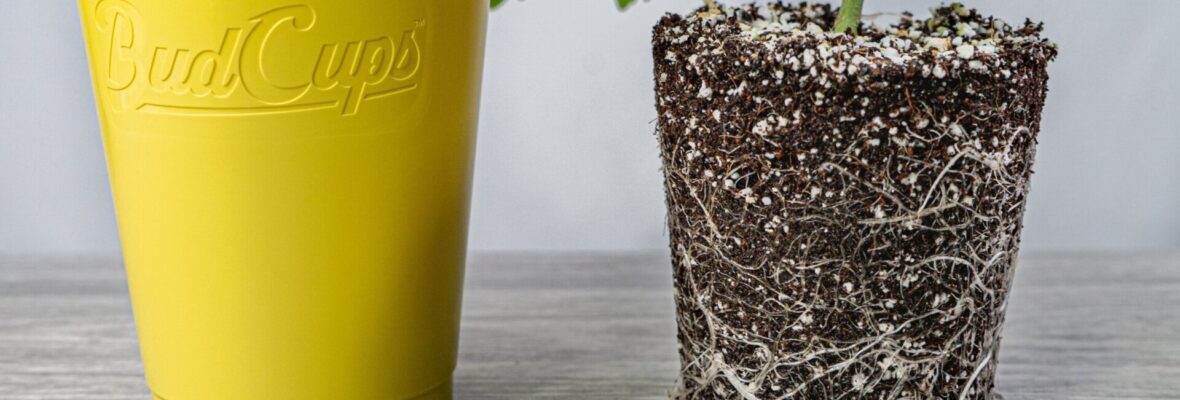
The future of farming doesn’t look like something out of a sci-fi movie; it is closer to home than you think, and it’s small—cups small, to be precise. Hydroponic growing cups, a modern approach to cultivating plants, are rapidly reshaping urban agriculture and vertical farming. While traditional soil-based agriculture has been the backbone of food production, it is facing increasing challenges such as urbanization, climate change, and limited arable land. Hydroponics, on the other hand, offers a sustainable and efficient method of growing crops, especially in urban environments.
In this article:
- Discover how this approach is offering a sustainable solution to the challenges faced by traditional agriculture, including urbanization, climate change, and the scarcity of arable land.
- Learn about the benefits of hydroponics in urban agriculture and vertical farming, including its efficiency and the potential for reducing water usage and carbon footprint.
- Explore real-world applications in transforming urban spaces into productive agricultural sites, contributing to food security and promoting green living.
The Hydroponic Revolution in Agriculture
What is Hydroponic Agriculture?
Hydroponic agriculture is a method of growing plants without soil, using mineral nutrient solutions in a water solvent. Plants that are grown hydroponically may be supported by an inert medium, like perlite or gravel, or held directly in the solution with their roots exposed. This system is finely tuned to deliver the exact nutrients that plants need, when they need them, and in the precise amounts. Hydroponic systems can be set up indoors or outdoors, making them an ideal choice for urban and vertical farming.
The Advantages of Hydroponic Growing Systems
- Water Conservation: Hydroponic systems use water more efficiently, with some estimates suggesting up to 90% less water is used compared to traditional soil-based agriculture.
- No Soil Erosion: Traditional farming methods can lead to significant soil erosion, whereas hydroponics eliminates this issue entirely.
- Reduced Space Requirements: Hydroponic systems can be stacked vertically, allowing for greater production per square meter.
- Control Over Growing Conditions: Hydroponic systems are closed-loop and can be closely monitored and adjusted, leading to increased productivity and less spoilage.
The Role of Urban Agriculture in Food Security
Why Urban Agriculture?
Urban agriculture is becoming increasingly important as more of the global population shifts to urban areas. It helps to minimize the distance food must travel from farm to table, reducing the carbon footprint associated with transportation. Furthermore, urban farming can provide jobs, improve access to fresh produce, and offer education on food production. This approach fit perfectly into this model, enabling a farm-to-table movement that can thrive in even the most space-constrained urban locales.
The Challenges of Urban Agriculture
- Limited Space: In dense urban environments, finding space for traditional farming can be a significant hurdle. Vertical farming and hydroponic systems offer solutions that require minimal space.
- Environmental Constraints: Urban areas often suffer from air and soil pollution, which can be mitigated through closed-loop hydroponic systems that reduce exposure to external pollutants.
- Access to Resources: Urban farmers face challenges with accessing land, water, and power, which are all critical for traditional agriculture. Hydroponic systems can reduce these barriers by allowing for farming almost anywhere with minimal resources.
Understanding Hydroponic Growing Cups
How Do Hydroponic Cups Work?
Hydroponic cups are a type of vessel or container designed specifically for hydroponic systems. They are generally made of a durable, nonporous material that is inert, such as plastic, and come in various shapes and sizes to accommodate different plant types. The cups are filled with a growing medium—from clay pebbles to vermiculite—to support the plant and its roots. The nutrient solution is then delivered directly to the roots, or the cup is placed in a larger hydroponic system where a nutrient-rich water solution circulates.
The Components of a Hydroponic Growing Cup
- Container: The base of the cup, which holds the growing medium and provides stability for the plant.
- Growing Medium: The substance that supports the plant and its roots and facilitates the delivery of the nutrient solution.
- Root Module: The section of the cup where the plant’s roots are housed and have access to the nutrient solution.
The Adaptability of Hydroponic Growing Cups
Versatility in Plant Growth
Hydroponic systems are incredibly versatile, capable of growing a wide variety of crops. From leafy greens and herbs to fruiting plants like tomatoes and peppers, the adaptability of this approach makes it possible to grow almost anything, anywhere. The ability to control the growing environment down to the slightest detail means that crops are consistently of high quality, regardless of seasonal variability.
Benefits for Small-Scale Farmers
Small-scale and urban farmers benefit greatly from the use of hydroponic systems. They can be set up indoors or on rooftops, reducing the need for large tracts of farmland. Hydroponics requires less water and space than traditional farming, making it feasible for small urban operations to thrive in local markets. This equips small farmers with a sustainable, year-round growing tool that is not reliant on the erratic conditions of nature.
The Effect on Food Quality and Safety
Enhanced Quality Through Controlled Conditions
The controlled nature of hydroponic systems leads to enhanced food quality. Plants receive the right amount of light, water, and nutrients throughout their growth, which translates into better tasting and more nutritious produce. Additionally, the absence of soil reduces the likelihood of contamination by common pathogens, contributing to improved food safety.
Implications for Organic and Locally Grown Food
Hydroponics can be used with organic practices, and the absence of soil means that less organic matter is needed. This makes it an attractive method for producing organic foods in urban settings. The ability to grow food locally also supports sustainable agriculture, reducing the need for long-distance transportation and the associated environmental costs.
Maximizing Production with Vertical Farming
How Do Hydroponic Cups Fit into Vertical Farming?
Vertical farming takes agriculture to new heights, quite literally. By stacking hydroponic systems on top of each other, it’s possible to dramatically increase production while using a small footprint. Hydroponic cups are a crucial element of this system, as they are designed to be compact and efficient. They can be stacked in columns or arranged on shelves, making the most of the available space.
The Impact on Urban Development
The integration of hydroponic systems and vertical farming into urban development can significantly impact the sustainability of cities. It reduces the need to import food from rural areas and can even help to repurpose unused urban spaces. By producing food locally, cities can support a more circular economy that minimizes waste and carbon emissions.
Conclusion
Hydroponic farming is not a silver bullet that will solve all the challenges facing modern agriculture. However, it is a significant piece of the puzzle, especially when it comes to urban agriculture and the increasing demand for locally grown, high-quality produce. The use of hydroponic growing cups is an innovation that holds tremendous promise for the future of farming—a future that is sustainable, efficient, and deeply rooted in the communities it serves. The technology may be small, but its potential to change the world of agriculture is immeasurable.


